Adopting MBSE - A Case Study
By Dr. Paulin Kantue
By adopting MBSE and digital twin technologies, European industries can achieve significant cost savings, improve operational efficiency, and contribute to broader sustainability objectives. Learn more
Problem Definition
A high-value machine breaks down ahead of schedule, creating frustration for maintenance engineers.
The machine has visible damage, like rust, loose parts, or smoke. None which was recorded in the previous maintenance report.


Requirement Analysis
Instead of the usual whiteboard or Excel spreadsheet with list of issues, dates and links, a framework for collecting data is adopted.
Data of all critical components is discussed, collected and used to establish cause-effect relationships.
Model Creation
Engineers develop a digital twin of the machine, integrating real-time sensor data and simulations to predict failures before they happen.
This virtual model is tested under different conditions to optimize maintenance strategies.

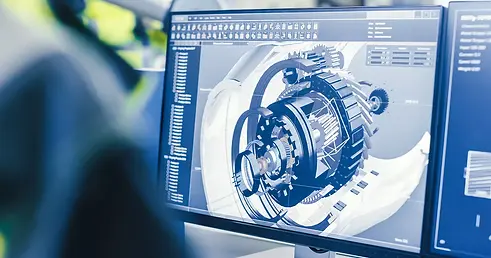
System Design & Optimization
Using insights from the digital twin, engineers redesign key components and implement predictive maintenance algorithms to enhance efficiency and reduce breakdowns.
IoT sensors and AI-driven diagnostics are integrated into the system.
Implementation & Testing
The newly optimized machine components and predictive maintenance system are installed in a real-world setting.
Engineers conduct live tests to compare performance with previous maintenance models.


Deployment & Continuous Monitoring
The system is fully deployed, and continuous monitoring is performed via IoT dashboards that alert engineers before failures occur.
AI-based analytics continuously refine maintenance schedules.